Metric mania lesson 1 length – Welcome to Metric Mania Lesson 1: Length! In this lesson, we’ll dive into the importance of establishing clear and concise metrics for project success. We’ll explore the difference between effective and ineffective metrics, discuss the potential consequences of using too many or too few metrics, and provide a framework for developing a metrics framework that aligns with your project goals.
Metric Mania Lesson 1 Length
Establishing clear and concise metrics is crucial for project success. Metrics provide objective, quantifiable measures of progress and outcomes, enabling teams to track performance, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions.
Effective metrics are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). They focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with project objectives and provide actionable insights. For example, a marketing campaign may track website traffic, conversion rates, and customer engagement as metrics of success.
Ineffective Metrics
Ineffective metrics, on the other hand, are often vague, subjective, or difficult to measure. They may not provide meaningful insights or lead to actionable steps. For instance, tracking the “number of meetings held” may not be an effective metric if it does not consider the quality or outcomes of those meetings.
Consequences of Too Many or Too Few Metrics
Using too many metrics can overwhelm teams and make it difficult to focus on what matters most. It can lead to data overload and confusion, hindering effective decision-making. Conversely, using too few metrics may not provide a comprehensive view of project performance and limit the ability to identify areas for improvement.
Finding the right balance is essential. A well-defined set of SMART metrics enables teams to track progress, make data-driven decisions, and ultimately achieve project goals.
Metrics Framework

A metrics framework is a structured approach to defining, collecting, and analyzing data that can be used to track progress towards goals. When developing a metrics framework, it is important to align the metrics with the project goals, so that the data collected is relevant and meaningful.
There are three main types of metrics: input, output, and outcome metrics.
Input Metrics
Input metrics measure the resources that are put into a project. This could include things like the number of hours worked, the amount of money spent, or the number of people involved.
Output Metrics, Metric mania lesson 1 length
Output metrics measure the results of a project. This could include things like the number of products produced, the number of customers acquired, or the amount of revenue generated.
Outcome Metrics
Outcome metrics measure the impact of a project. This could include things like the increase in customer satisfaction, the decrease in churn rate, or the improvement in employee morale.
It is important to use a mix of input, output, and outcome metrics to get a complete picture of a project’s progress. Input metrics can help you identify areas where you need to improve efficiency, output metrics can help you track progress towards goals, and outcome metrics can help you measure the impact of your work.
Metrics can be a powerful tool for tracking progress and making data-driven decisions. By developing a metrics framework that is aligned with your project goals, you can ensure that you are collecting the data you need to make informed decisions and improve your chances of success.
Data Collection and Analysis

Data collection and analysis are crucial for understanding project metrics and making informed decisions. Various methods exist for collecting data, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Accuracy and integrity of data are paramount. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading conclusions and poor decision-making. Techniques like data validation, data cleaning, and data normalization help ensure data quality.
Data Collection Methods
- Surveys:Collect data from a sample of the target population through questionnaires.
- Interviews:In-depth conversations with individuals to gather qualitative and quantitative data.
- Observation:Recording data directly by observing processes or behaviors.
- Document Analysis:Reviewing existing documents, such as project plans, meeting minutes, and reports.
- Historical Data:Using data collected from previous projects or industry benchmarks.
Data Analysis Techniques
Data analysis involves identifying trends and patterns to draw meaningful insights. Techniques include:
- Descriptive Statistics:Summarizing data using measures like mean, median, and standard deviation.
- Inferential Statistics:Drawing conclusions about a larger population based on a sample.
- Regression Analysis:Determining the relationship between variables and predicting future outcomes.
- Data Visualization:Creating graphs, charts, and dashboards to represent data in a visually appealing way.
Metrics Reporting
Metrics reporting is an essential part of project management. It allows you to track your progress, identify areas for improvement, and communicate your results to stakeholders. There are a number of different ways to report metrics, and the best approach will vary depending on your audience and the purpose of the report.
One common way to report metrics is to use a table. Tables are a great way to present data in a clear and concise way. They can be used to show trends over time, compare different metrics, or track progress against goals.
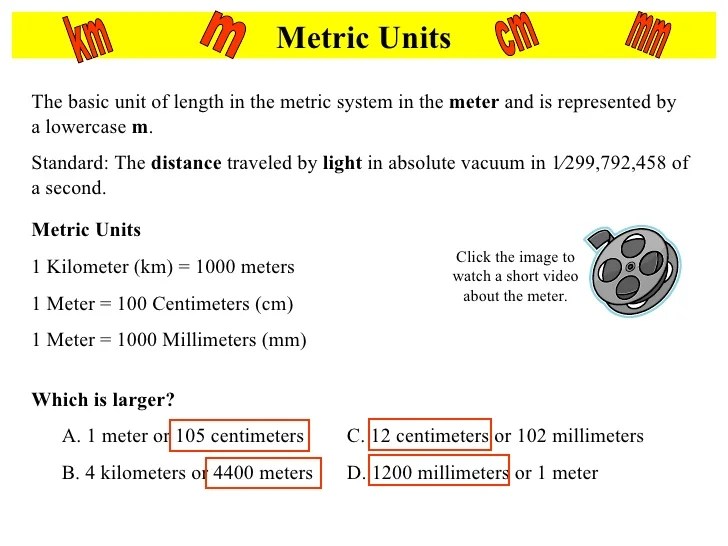
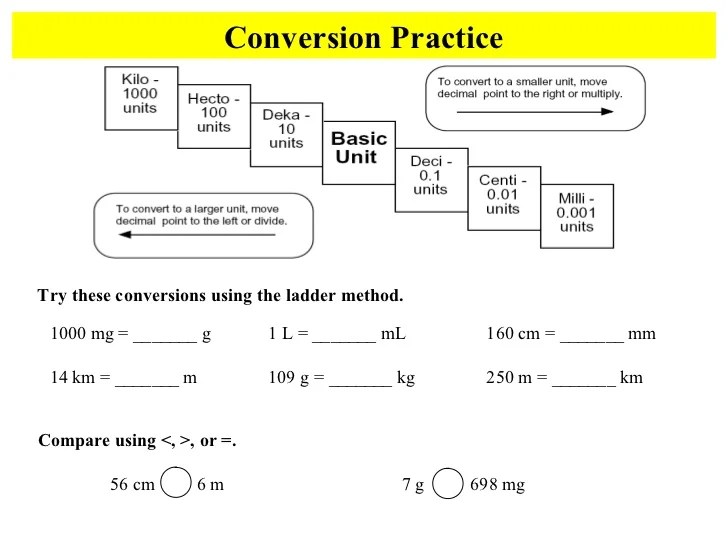
In Metric Mania Lesson 1, we’re diving into the fascinating world of length measurements. From centimeters to kilometers, we’ll master the art of converting between units. But if you ever get lost in a sea of equations, remember the net ionic equation for HCN + KOH ( hcn + koh net ionic equation ). It’s like a compass, guiding you back to the shores of metric mania and keeping you on track in your length measurement adventures.
Another way to report metrics is to use a chart or graph. Charts and graphs can be a great way to visualize data and make it easier to see trends and patterns. They can also be used to compare different metrics or track progress against goals.
When reporting metrics, it is important to tailor the report to your audience. For example, if you are reporting to a technical audience, you may want to use more technical language and include more detailed data. If you are reporting to a non-technical audience, you may want to use more plain language and focus on the key findings.
Metrics can be a powerful tool for communicating project status and progress. By reporting metrics effectively, you can keep stakeholders informed, identify areas for improvement, and make better decisions.
Using Metrics to Communicate Project Status and Progress
Metrics can be used to communicate project status and progress in a number of ways. For example, you can use metrics to:
- Track progress against goals
- Identify areas for improvement
- Make better decisions
- Keep stakeholders informed
When using metrics to communicate project status and progress, it is important to choose the right metrics and report them in a clear and concise way. You should also make sure that your metrics are aligned with your project goals and that you are tracking them consistently.
Continuous Improvement: Metric Mania Lesson 1 Length

Metrics play a crucial role in continuous improvement processes. They provide objective and quantifiable data that helps organizations identify areas for improvement, track progress, and make informed decisions. By analyzing metrics, organizations can pinpoint inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and opportunities for optimization.
Using Metrics to Identify Areas for Improvement
Metrics can be used to identify areas for improvement in several ways:
-
-*Compare performance against benchmarks
By comparing current performance to industry standards or historical data, organizations can identify areas where they are falling short and need to improve.
-*Track trends over time
Analyzing metrics over time can reveal trends and patterns that indicate potential areas for improvement. For example, if customer satisfaction ratings have been declining over time, it may indicate a need to address customer experience issues.
-*Analyze customer feedback
Customer feedback can provide valuable insights into areas where improvements can be made. By collecting and analyzing customer feedback, organizations can identify specific areas where their products or services are not meeting customer expectations.
Key Questions Answered
What are the benefits of using metrics?
Metrics provide a way to track progress, measure success, and identify areas for improvement. They can help you make data-driven decisions, communicate project status, and ensure that your project is on track to meet its goals.
How do I choose the right metrics for my project?
The best metrics for your project will depend on your specific goals and objectives. However, some general tips include choosing metrics that are relevant, measurable, actionable, and time-bound.
How often should I track my metrics?
The frequency of tracking will depend on the type of metric and the project timeline. However, it’s generally a good idea to track metrics regularly, such as weekly or monthly, to ensure that you’re staying on track and can make adjustments as needed.
