Atoms isotopes and ions worksheet – Delve into the fascinating world of atoms, isotopes, and ions with our comprehensive Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions Worksheet. This engaging resource provides a thorough overview of these fundamental building blocks, their properties, and their diverse applications across various scientific disciplines.
Through interactive exercises, calculations, and real-world examples, this worksheet empowers learners to grasp the concepts of atomic structure, isotopic variations, and ionic behavior. Its comprehensive content caters to students, educators, and anyone seeking to deepen their understanding of the foundational elements of matter.
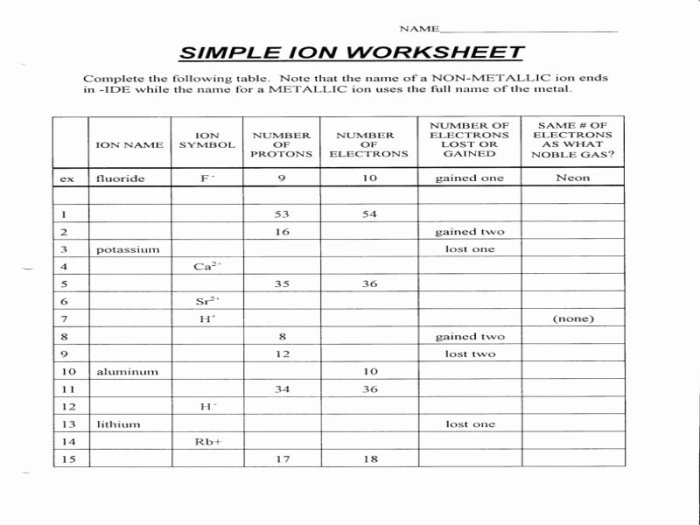
Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions: Atoms Isotopes And Ions Worksheet
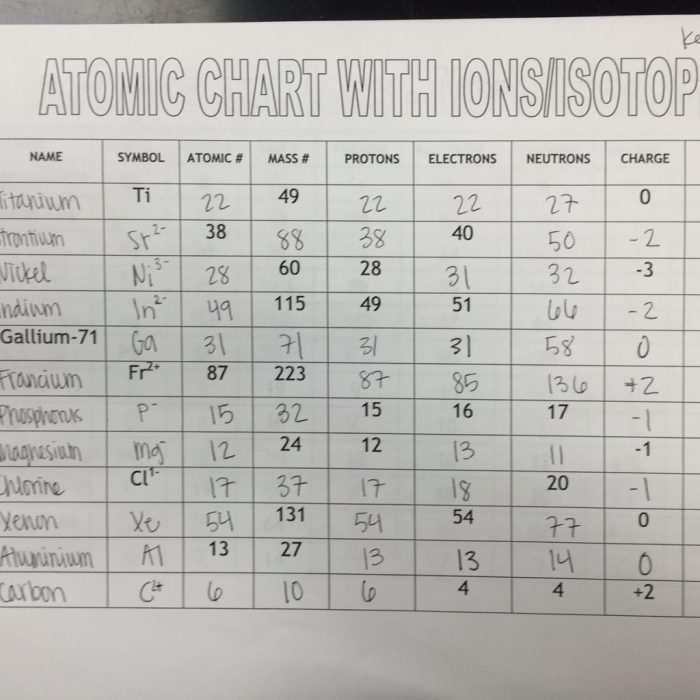
Atoms, isotopes, and ions are fundamental components of matter and play crucial roles in various scientific disciplines.
1. Define Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions, Atoms isotopes and ions worksheet
An atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. It consists of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same atomic number (number of protons) but different neutron numbers. They have identical chemical properties but different masses.
Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net electrical charge.
2. Properties of Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions
The properties of atoms are determined by their atomic number, mass number (sum of protons and neutrons), and electron configuration (arrangement of electrons in energy levels).
Isotopes have different masses due to varying neutron numbers, which can affect their physical properties such as density and melting point.
Ions have a net charge (positive or negative) and can have different chemical reactivity compared to their neutral counterparts.
3. Applications of Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions
- Atoms are used in various fields, including medicine (radioactive isotopes for imaging and therapy), energy (nuclear power), and materials science (semiconductors).
- Isotopes find applications in nuclear medicine (radioactive isotopes for diagnosis and treatment), archaeology (carbon dating), and environmental science (isotope ratios for studying climate change).
- Ions play a role in electrochemistry (electroplating, batteries), biology (ion channels, pH regulation), and industrial processes (electrolysis, water treatment).
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key differences between atoms, isotopes, and ions?
Atoms are the fundamental units of matter, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, resulting in variations in mass. Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, acquiring an electrical charge.
How are isotopes used in practical applications?
Isotopes have numerous applications, including nuclear medicine (e.g., iodine-131 for thyroid imaging), archaeology (e.g., carbon-14 dating), and environmental science (e.g., tracing pollutants using stable isotopes).
What is the significance of ions in biological processes?
Ions play crucial roles in biological systems, regulating nerve impulses, maintaining fluid balance, and facilitating chemical reactions essential for life.