Welcome to the fascinating world of genetics, where the Pea Plant Punnett Square Worksheet Answers unravel the secrets of inheritance and empower you with the knowledge to predict the outcome of genetic crosses. Dive into this comprehensive guide and witness the power of Punnett squares in unraveling the mysteries of genetic inheritance.
This guide will take you on an enlightening journey through the fundamentals of genetics, exploring the concepts of genotypes and phenotypes, dominant and recessive alleles, homozygous and heterozygous genotypes, and the probability of inheritance. Along the way, you’ll discover the practical applications of Punnett squares in plant breeding and genetic research, gaining a deeper understanding of how scientists use this powerful tool to predict the outcome of genetic crosses.
Pea Plant Punnett Square: Pea Plant Punnett Square Worksheet Answers

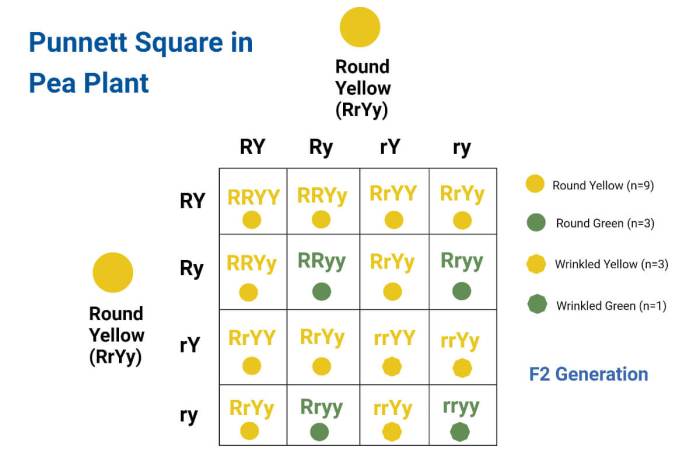
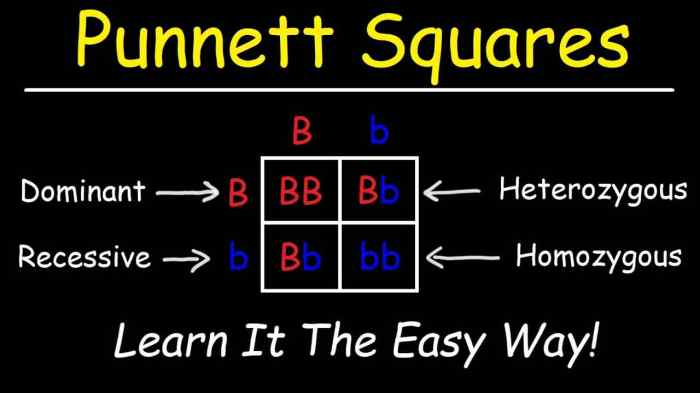
A Punnett square is a diagram that predicts the probability of inheriting specific traits in offspring. It is used in genetics to determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of their parents.
A Punnett square is a grid with two axes, one for each parent. The top axis represents the possible alleles for one parent, and the side axis represents the possible alleles for the other parent. The squares in the grid represent the possible genotypes of the offspring.
Genotypes and Phenotypes
A genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism. It is determined by the alleles that the organism inherits from its parents. A phenotype is the observable characteristics of an organism, such as its height, eye color, or flower color.
Genotypes determine phenotypes. For example, in pea plants, the genotype for flower color is determined by two alleles, one from each parent. The dominant allele (P) codes for purple flowers, and the recessive allele (p) codes for white flowers. A pea plant with the genotype PP will have purple flowers, a pea plant with the genotype pp will have white flowers, and a pea plant with the genotype Pp will have purple flowers (because the dominant allele masks the recessive allele).
Dominant and Recessive Alleles
A dominant allele is an allele that is expressed in the phenotype of an organism, even if the organism only has one copy of the allele. A recessive allele is an allele that is only expressed in the phenotype of an organism if the organism has two copies of the allele.
In the example above, the allele for purple flowers (P) is dominant, and the allele for white flowers (p) is recessive. This means that a pea plant with the genotype Pp will have purple flowers, even though it only has one copy of the dominant allele.
Homozygous and Heterozygous Genotypes
A homozygous genotype is a genotype in which both alleles are the same. A heterozygous genotype is a genotype in which the two alleles are different.
In the example above, a pea plant with the genotype PP is homozygous dominant for flower color. A pea plant with the genotype pp is homozygous recessive for flower color. A pea plant with the genotype Pp is heterozygous for flower color.
Probability of Inheritance, Pea plant punnett square worksheet answers
Punnett squares can be used to calculate the probability of inheriting specific traits in offspring. The probability of inheriting a particular genotype is determined by the frequency of the alleles in the population.
For example, if the frequency of the dominant allele (P) is 0.7 and the frequency of the recessive allele (p) is 0.3, then the probability of inheriting the genotype PP is 0.49, the probability of inheriting the genotype Pp is 0.42, and the probability of inheriting the genotype pp is 0.09.
Applications of Punnett Squares
Punnett squares are used in a variety of applications, including plant breeding and genetic research. In plant breeding, Punnett squares can be used to predict the outcome of genetic crosses and to select for desired traits.
In genetic research, Punnett squares can be used to study the inheritance of traits and to identify the genes that are responsible for those traits.
FAQ Insights
What is a Punnett square?
A Punnett square is a diagram that predicts the possible genotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of their parents.
What is the purpose of a Punnett square?
Punnett squares are used to calculate the probability of inheriting specific traits in offspring.
What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype?
A genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism, while a phenotype is the observable characteristics of an organism.
What is the difference between a dominant allele and a recessive allele?
A dominant allele is an allele that is expressed in the phenotype even if only one copy is present, while a recessive allele is an allele that is only expressed in the phenotype if two copies are present.
What is the difference between a homozygous genotype and a heterozygous genotype?
A homozygous genotype is a genotype that has two identical alleles for a particular gene, while a heterozygous genotype is a genotype that has two different alleles for a particular gene.