Circuit training volumes of solids with known cross sections is a crucial aspect of exercise science that involves calculating the volume of solids using their known cross-sectional shapes. This concept plays a significant role in circuit training, where volume is a key factor in achieving fitness goals.
This guide will delve into the formulas, techniques, and programming considerations associated with circuit training volumes of solids with known cross sections, providing a comprehensive understanding of this important topic.
Understanding the volume of solids with known cross sections is essential for accurately determining the amount of material or substance present. By calculating the cross-sectional area and applying appropriate formulas, we can precisely determine the volume of various objects, which has applications in fields such as engineering, construction, and manufacturing.
Circuit Training Volumes of Solids with Known Cross Sections
In the realm of geometry and fitness, understanding the volume of solids with known cross sections plays a pivotal role. This article delves into the intricate relationship between volume calculations and circuit training, providing a comprehensive guide for fitness enthusiasts and students alike.
Volume Calculations
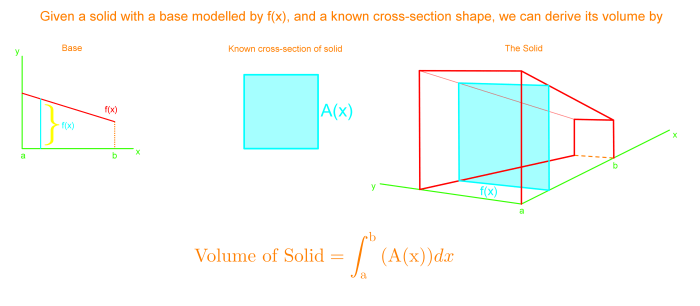
Calculating the volume of a solid with a known cross section involves determining the area of the cross section and multiplying it by the length of the solid. Different cross-sectional shapes necessitate specific formulas:
- Rectangle:Area = length × width
- Triangle:Area = 1/2 × base × height
- Circle:Area = π × radius²
Accurate measurement of the cross-sectional area is crucial for precise volume calculations.
Circuit Training
Circuit training, a popular fitness regimen, incorporates multiple exercises performed in succession with minimal rest. It relates to volume as it allows for the accumulation of a higher volume of work within a shorter timeframe.
Benefits of circuit training for increasing volume include:
- Increased caloric expenditure
- Improved muscular endurance
- Enhanced metabolic rate
Sample circuit training program incorporating volume exercises:
| Exercise | Sets | Repetitions | Rest |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squats | 3 | 12-15 | 60 seconds |
| Push-ups | 3 | 10-12 | 60 seconds |
| Lunges | 3 | 15-20 | 60 seconds |
| Plank | 3 | 30-60 seconds hold | 60 seconds |
Programming Considerations
Progressive overload is essential when programming for volume. Gradually increasing the weight, sets, or repetitions over time ensures continuous adaptation and progress.
Rest and recovery are integral to volume training:
- Adequate rest between sets:Allows for muscle recovery and energy replenishment.
- Rest days:Essential for overall recovery and to prevent overtraining.
Appropriate volume levels vary based on training goals:
- Beginner:Lower volume, focusing on technique and form.
- Intermediate:Moderate volume, aiming for muscle growth and strength gains.
- Advanced:High volume, pushing the limits for maximum performance.
Safety and Technique
Proper form and technique are paramount when performing volume exercises. Common mistakes that can lead to injury include:
- Excessive weight:Can strain muscles and joints.
- Incorrect posture:Can cause imbalances and pain.
- Overtraining:Can lead to burnout and injury.
Tips for staying safe while training with high volume:
- Start gradually:Gradually increase volume to allow the body to adapt.
- Warm up properly:Prepare muscles for the workout.
- Listen to your body:Rest when needed and avoid pushing through pain.
- Use proper form:Focus on correct technique to prevent injuries.
Nutrition and Recovery: Circuit Training Volumes Of Solids With Known Cross Sections
Adequate nutrition is crucial for supporting volume training. Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth, carbohydrates provide energy, and hydration is vital for overall performance.
Post-workout recovery strategies include:
- Protein intake:Consuming protein within 30 minutes after a workout aids in muscle recovery.
- Carbohydrate replenishment:Eating carbohydrates helps restore glycogen stores.
- Hydration:Drinking plenty of fluids is essential for rehydration and recovery.
- Sleep:Adequate sleep allows for muscle repair and hormone production.
Essential FAQs
What is the formula for calculating the volume of a solid with a known cross section?
The formula for calculating the volume of a solid with a known cross section is: Volume = Cross-sectional Area x Length
How does circuit training relate to volume?
Circuit training involves performing multiple exercises in a continuous sequence, which can help increase training volume by reducing rest periods and maximizing the number of exercises completed in a given time.
Why is it important to accurately measure the cross-sectional area when calculating volume?
Accurately measuring the cross-sectional area is crucial because it directly affects the calculated volume. Any errors in measuring the cross-sectional area will result in corresponding errors in the volume calculation.