Labor market participation ap human geography, a field of study that delves into the complexities of labor force dynamics, invites us on an intellectual journey to unravel the factors influencing individuals’ decisions to engage in paid work, the implications for economic growth and inequality, and the role of government policies in shaping labor market outcomes.
This comprehensive analysis promises a profound understanding of the interplay between labor force participation and various social, economic, and policy dimensions.
As we delve into the intricacies of labor market participation, we will examine historical trends and demographic variations, exploring the forces that drive individuals to enter or exit the labor force. We will uncover the profound impact of education, childcare availability, and family structure on shaping labor market participation patterns.
Labor Market Participation Trends: Labor Market Participation Ap Human Geography
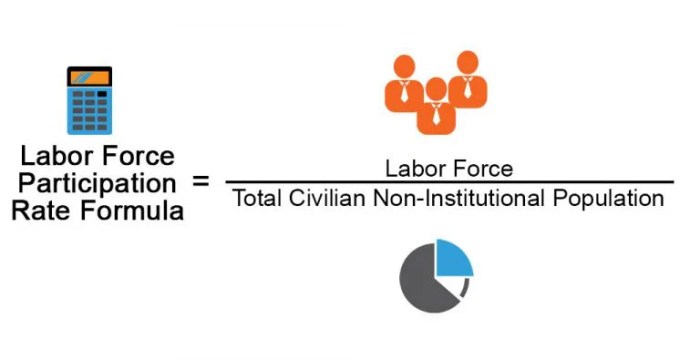
Labor force participation refers to the proportion of the working-age population that is employed or actively seeking employment. It is a key indicator of economic activity and reflects the supply of labor available in the economy. Historically, labor force participation rates have varied significantly across different demographic groups.
In the past, men have typically had higher labor force participation rates than women. However, in recent decades, women’s labor force participation has increased substantially in many countries. This is due in part to factors such as increased educational attainment, changes in family structure, and government policies aimed at promoting gender equality in the workplace.
Factors Influencing Labor Market Participation, Labor market participation ap human geography
A variety of factors influence labor force participation decisions, including economic, social, and cultural factors.
- Economic factors:The availability of jobs, wages, and benefits can influence whether individuals choose to participate in the labor force. When jobs are plentiful and wages are high, labor force participation tends to increase. Conversely, when jobs are scarce and wages are low, labor force participation may decline.
- Social factors:Family structure, childcare availability, and cultural norms can also affect labor force participation. For example, individuals with young children may be less likely to participate in the labor force if childcare is not readily available or affordable.
- Cultural factors:Cultural norms and values can influence whether individuals view labor force participation as an acceptable or desirable option. In some cultures, women may be discouraged from participating in the labor force due to traditional gender roles.
Question Bank
What is the labor force participation rate?
The labor force participation rate is the percentage of the working-age population that is employed or actively seeking employment.
What factors influence labor market participation?
Labor market participation is influenced by a range of factors, including economic conditions, education levels, childcare availability, and family structure.
How does labor market participation affect economic growth?
Increased labor market participation can contribute to economic growth by increasing the size of the labor force and boosting productivity.
What is the relationship between labor market participation and inequality?
Labor market participation can have a complex relationship with inequality, as it can both increase and decrease income disparities depending on the specific context.
How do government policies affect labor market participation?
Government policies, such as minimum wage laws, paid family leave, and childcare subsidies, can influence labor market participation rates.